Explore the principles of balanced plate composition and understand how macronutrient distribution influences nutrition and eating patterns.
Educational content only. No promises of outcomes.
Explore the Details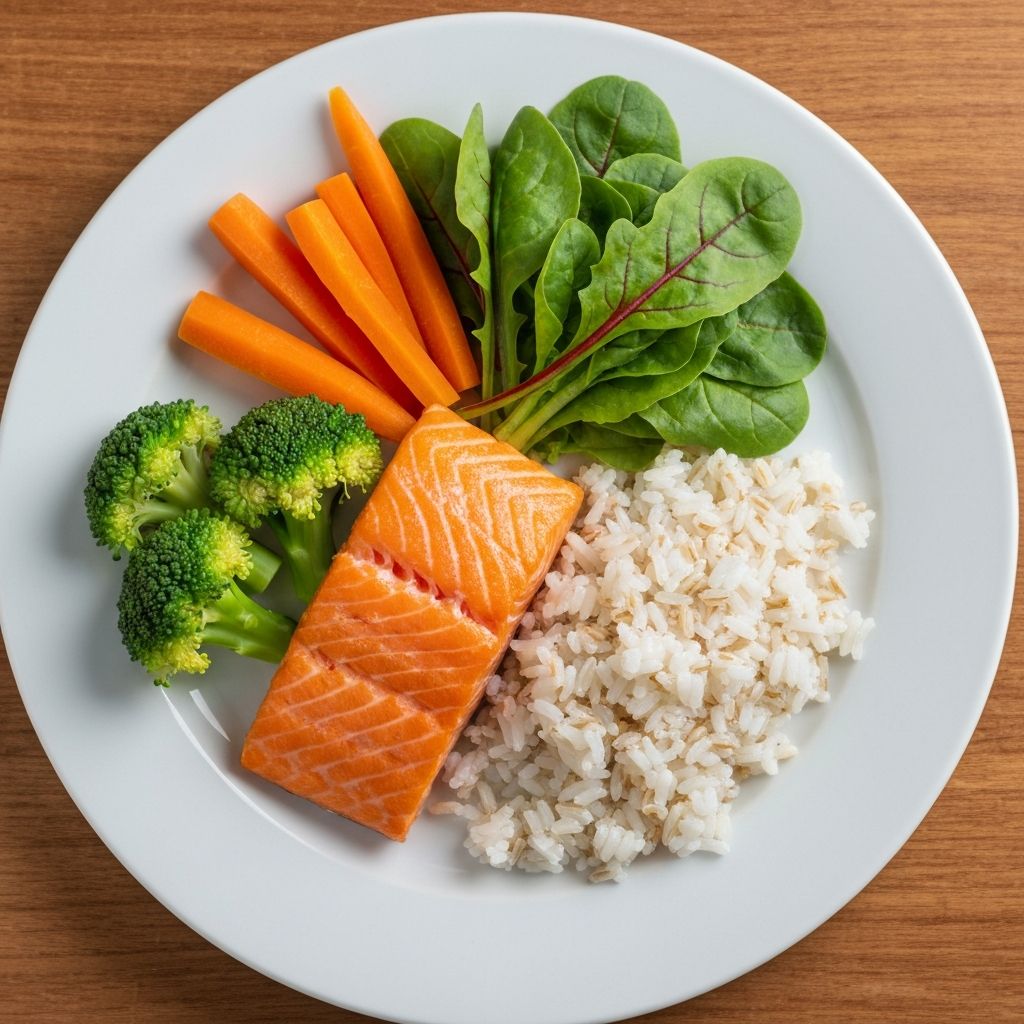
A balanced plate represents a conceptual framework for understanding how different food groups can be combined to create meals with varied macronutrient profiles. This approach examines the proportions of vegetables, proteins, and whole grains and their roles in overall nutrient intake.
Research in nutritional science describes how varying proportions of macronutrients on a plate influence satiety mechanisms, nutrient absorption, and physiological responses to meals. The concept explores the interplay between:
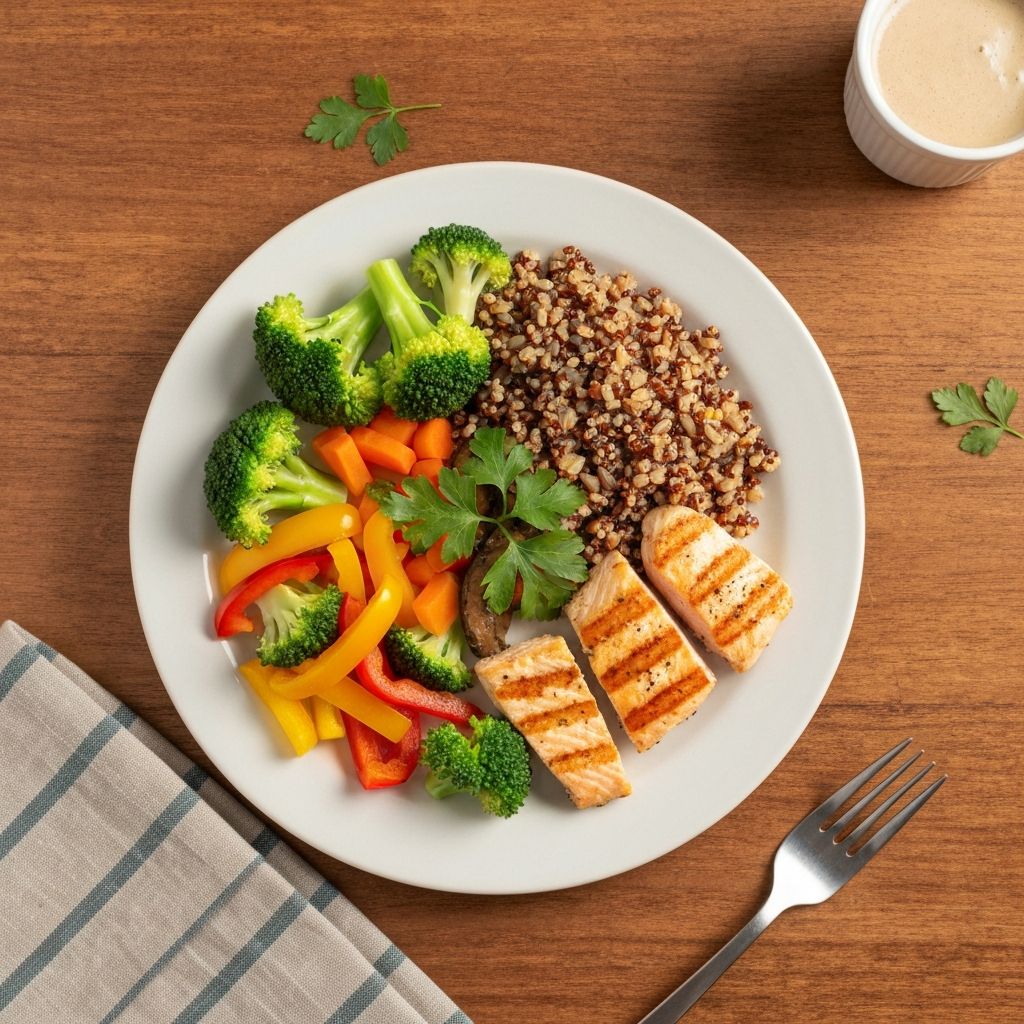
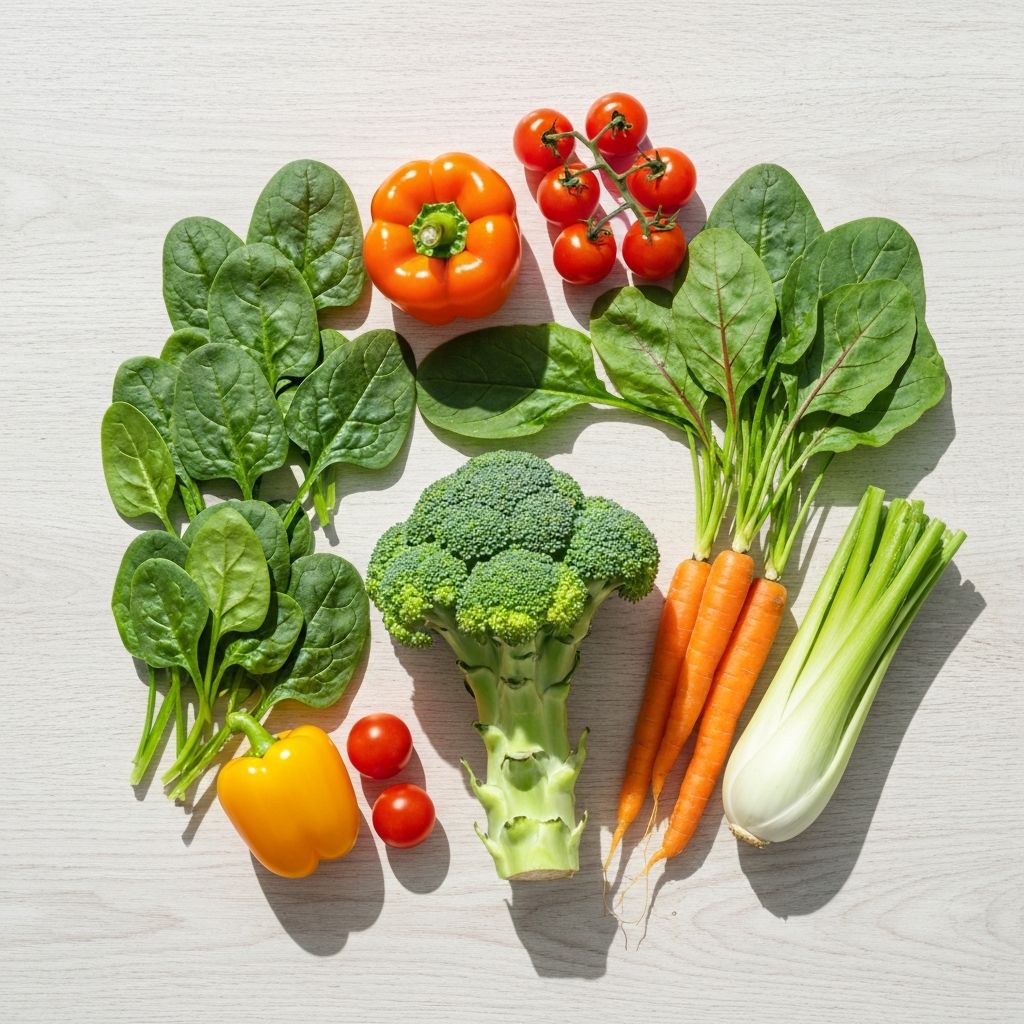


Scientific literature suggests that emphasizing vegetables on a plate contributes to increased micronutrient intake and enhanced satiety due to their fiber content and volume. Vegetables are rich in:
Population-level observations indicate that diets emphasizing plant-based foods show associations with sustained satiety and nutrient adequacy across diverse demographics.
Understanding different protein sources provides context for meal composition decisions. Both animal and plant-based proteins contribute amino acids essential for various physiological functions.
| Protein Source | Type | Nutritional Notes | Culinary Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salmon | Animal | Omega-3 fatty acids, B vitamins | Baking, grilling, poaching |
| Chicken Breast | Animal | Lean protein, B6, selenium | Roasting, sautéing, grilling |
| Lentils | Plant | Fiber, iron, polyphenols | Soups, salads, side dishes |
| Tofu | Plant | Complete protein, isoflavones | Stir-frying, baking, blending |
| Eggs | Animal | Complete amino acid profile, choline | Boiling, frying, baking |
| Chickpeas | Plant | Protein, fiber, minerals | Hummus, curries, roasting |
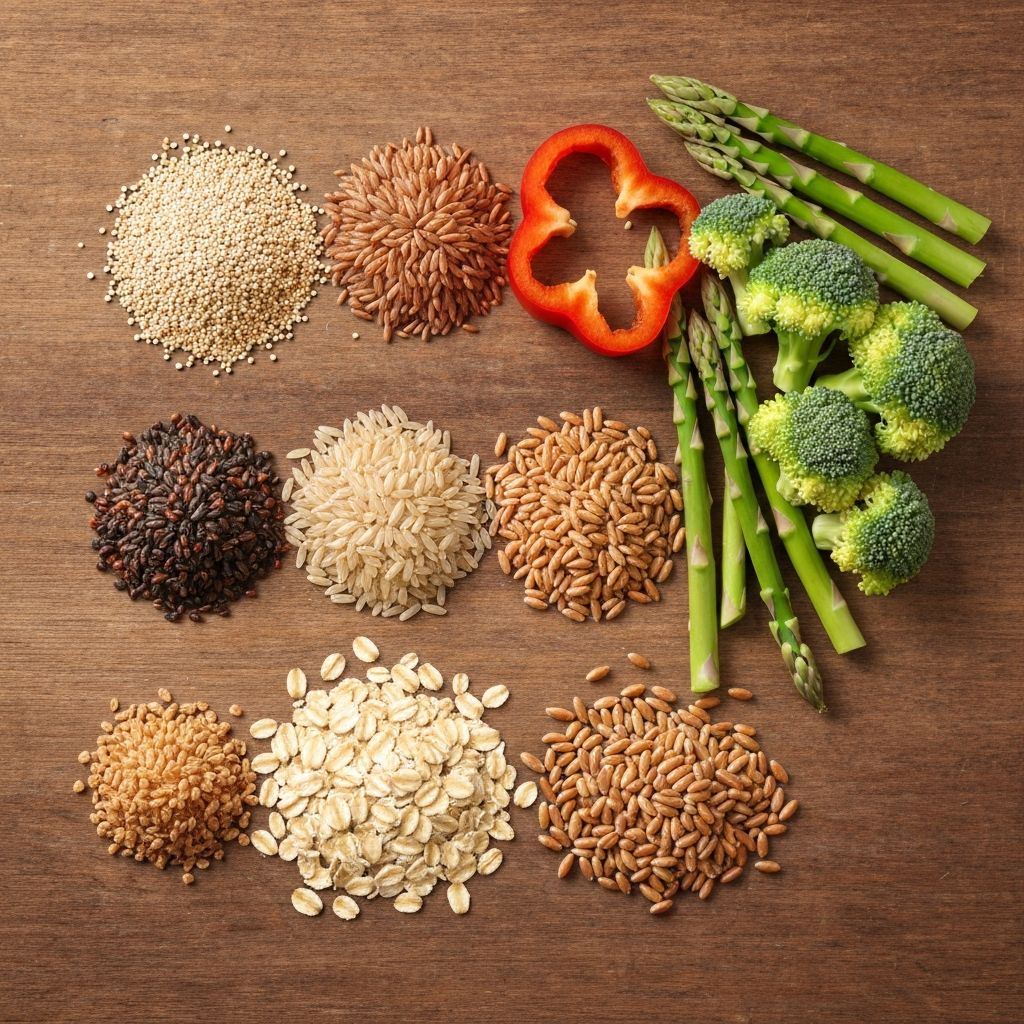
Whole grains differ from refined grains in their nutrient composition and physiological effects. Research examines how the intact fiber, bran, and germ layers in whole grains influence blood glucose responses and sustained energy availability.
Key aspects explored in nutritional science include:
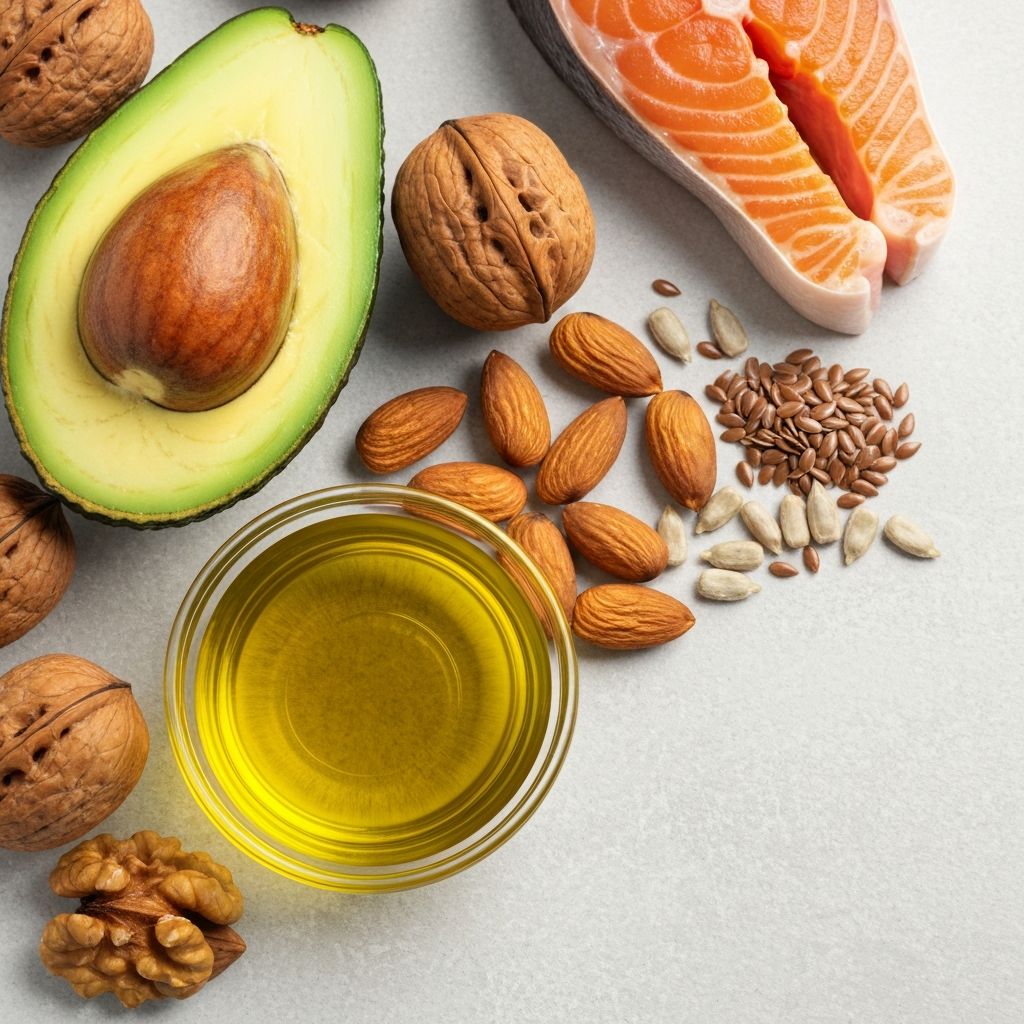


Different dietary fats play distinct roles in physiological processes. Beyond energy provision, fats support hormone synthesis, nutrient absorption, and nervous system function.
Unsaturated fats including polyunsaturated and monounsaturated varieties are found in nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish. Research indicates these fats support cardiovascular function and inflammatory responses.
Saturated fats contribute to cellular structure and vitamin absorption. Nutritional science explores their roles within balanced eating patterns.
The composition and type of dietary fats on a plate influences satiety signaling and nutrient bioavailability across the gastrointestinal tract.
Reality: Individual nutritional needs vary based on activity level, age, metabolism, and health status. Balanced plates represent general principles, not prescriptive requirements.
Reality: Carbohydrates serve essential roles in energy production and neurological function. The source and type matter more than simple quantity.
Reality: Different fat types have distinct physiological effects. Scientific evidence supports the inclusion of unsaturated fats in balanced eating patterns.
Reality: Balanced principles can accommodate diverse cuisines and preferences. Pleasure in eating remains compatible with nutritional awareness.
Dive deeper into the science of plate composition through our curated articles examining research findings and nutritional principles.

Explore what current scientific research reveals about macronutrient distribution and plate composition principles.
View All Articles →
Understanding the evidence behind recommended proportions of different food groups on a plate.
Read More →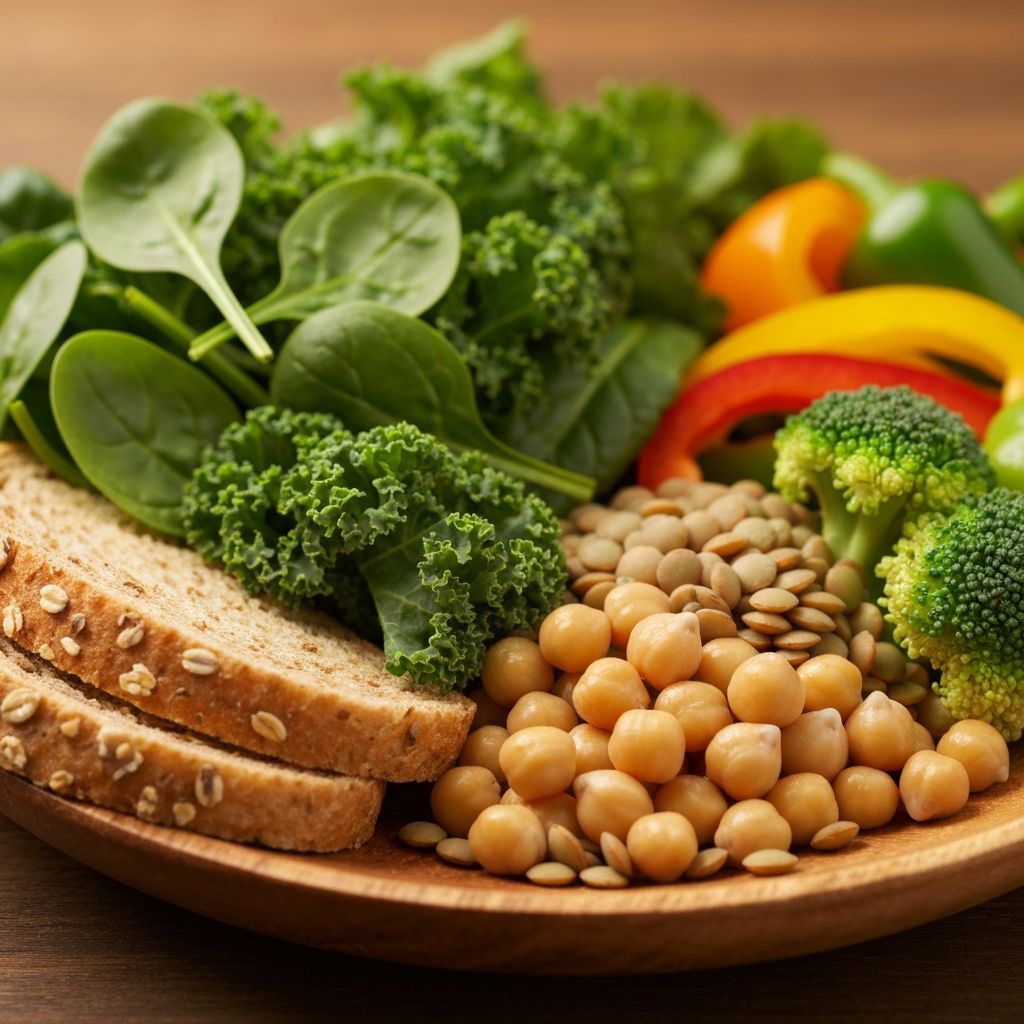
Examining the physiological mechanisms linking plate composition to feelings of fullness and satisfaction.
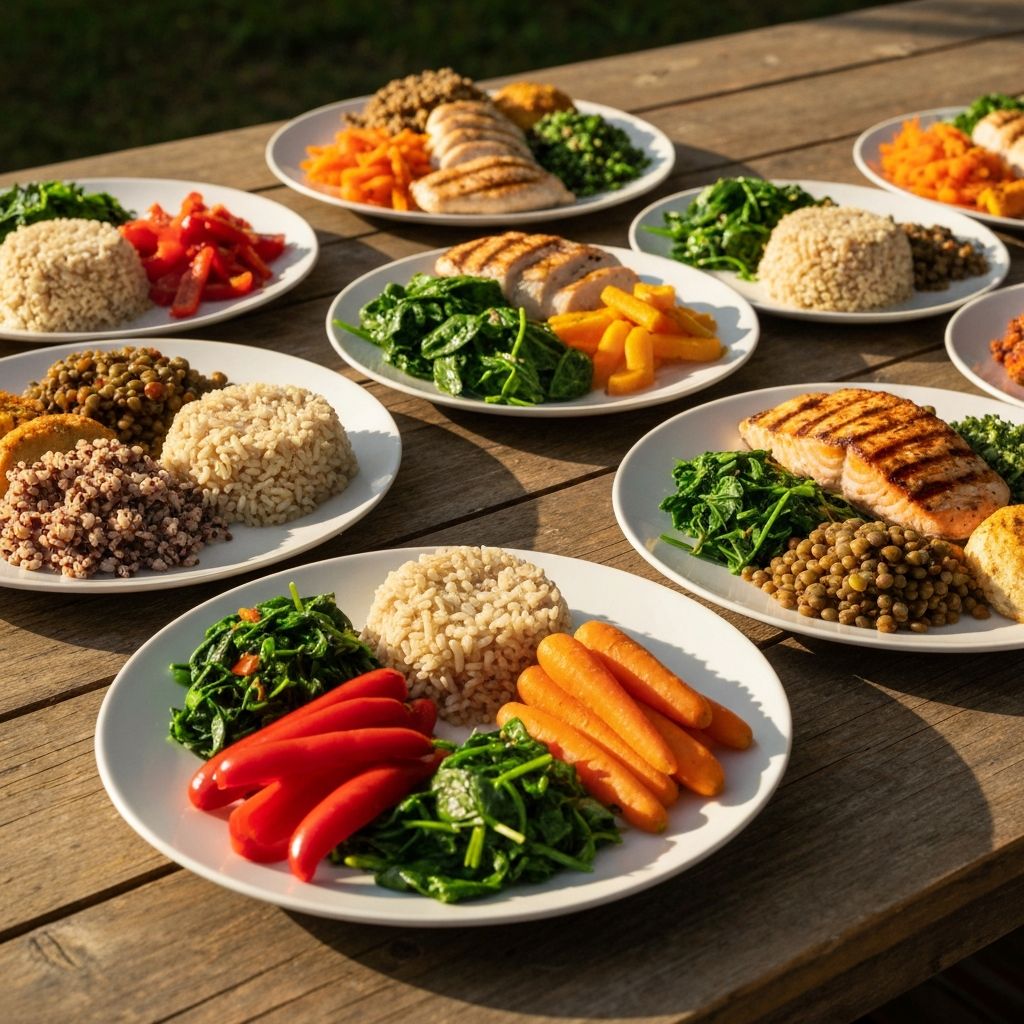
Read More →A balanced plate is a conceptual framework showing how different food groups might be proportioned in a meal. Typically depicted with vegetables comprising roughly half the plate, and the remaining half divided between protein sources and whole grains. This framework exists to help conceptualize nutrient diversity, not as a rigid prescription.
Scientific literature explores relationships between plate composition and satiety mechanisms. Vegetables contribute volume and fiber, protein influences satiation signaling, and whole grains provide sustained energy. These interactions merit individual consideration based on personal responses.
Yes, various cultures and nutritional frameworks offer different visual models for balanced meals. These reflect regional food availability, cultural preferences, and different nutritional approaches. No single model applies universally.
Macronutrients—carbohydrates, proteins, and fats—serve distinct physiological functions. Carbohydrates provide energy, proteins support tissue synthesis, and fats facilitate hormone production and nutrient absorption. Balanced proportions explore how these work together.
Dietary fiber influences digestive processes by slowing gastric emptying, promoting beneficial bacterial growth in the colon, and contributing to feelings of fullness. Different fiber types from various plant sources have different physiological effects.
Balanced plate concepts can be adapted to various dietary patterns including vegetarian, vegan, gluten-free, and others. The underlying principle of nutrient diversity can be achieved through different ingredient choices based on individual needs and preferences.
Portion size considerations remain individually variable. Plate models typically focus on proportions rather than absolute amounts. Personal energy needs, activity levels, and metabolism differ across individuals and time periods.
Cooking methods affect nutrient bioavailability, texture, and palatability. Steaming, roasting, and boiling influence micronutrient retention differently. Preparation choices interact with food composition to determine overall nutritional value.
Explore our comprehensive blog articles to deepen your understanding of nutrition science and plate composition principles.
Discover the Science